Egyptian Arabic
Learn Egyptian with real world videos, interactive captioning, and fun exercises!
Learning the Egyptian dialect of Arabic differs somewhat from acquiring Modern Standard Arabic, a distinction that becomes particularly significant for those looking to learn it online. Playaling is designed to help you master it quickly and easily, ensuring the process is both enjoyable and engaging. Our real world videos, complete with transcripts and interactive games, transform learning Egyptian Arabic into a fascinating adventure.

How can you learn Egyptian dialect?
Learning the Egyptian Arabic dialect presents a unique educational journey, distinct from the process taken when learning Modern Standard Arabic (MSA). Due to the relatively flexible grammatical structure of Egyptian Arabic compared to the more structured framework of MSA, learners are advised to prioritize practical engagement over theoretical study. This approach underscores the importance of direct interaction, attentive listening, and active speaking practices.
Hearing the Egyptian dialect firsthand plays a pivotal role. It bridges the gap between familiar textual elements of the Arabic script and the auditory nuances of the spoken language, which is necessary for those trying to learn Egyptian Arabic online. This sensory integration aids a deeper comprehension by linking phonetic sounds with their corresponding letters and, importantly, their meanings. Engaging with the language in this way—where listening activities are supported by visual associations with text—enhances the learning experience, promoting a comprehensive grasp of the dialect. This approach is in perfect harmony with the educational philosophy we advocate here at Playaling!
Various methods can be followed to achieve satisfactory results in learning the Egyptian dialect:
Regularly practice listening to Egyptian Arabic
A fundamental strategy involves immersing oneself in the sounds and rhythms of the dialect. This can be effectively accomplished by delving into the rich world of Egyptian culture through its music, movies, television series. Playaling offers an extensive collection of Egyptian cinematic and artistic productions, serving as an invaluable resource. By integrating these materials into your Egyptian Arabic learning process, Playaling supports not only the mastery of the Egyptian dialect but also provides an enriching experience of the prolific Egyptian entertainment landscape, celebrated throughout the Arab world.
Speak with native speakers
Upon advancing your proficiency in Egyptian Arabic through Playaling, it is highly recommended to engage in conversations with native speakers. This pivotal step allows you to apply and verify the knowledge acquired, interacting directly with those who use the dialect as their primary mode of communication.

Use language apps, courses, or online resources
Playaling offers a comprehensive suite of resources tailored for learners of the Egyptian dialect, including videos, transcriptions, and interactive exercises. It stands out by immersing users in authentic linguistic and cultural contexts, thereby making the learning process both engaging and effective. Playaling is ideal for those seeking to delve into Egyptian Arabic, providing a path from basic vocabulary to complex conversations, all while ensuring a deep cultural understanding.
Engage with materials written in Egyptian Arabic
Despite the prevalence of writing books, poetry, and novels in Modern Standard Arabic, the Egyptian dialect has broken this rule by appearing in many written materials. This trend not only enriches Arabic’s general diversity but also significantly aids those trying to learn Egyptian dialect. Playaling leverages this cultural richness by offering real-world videos in Egyptian dialect, complete with transcripts. This approach connects learners directly to the living language as it’s spoken today, enhancing understanding and fluency by exposing them to the dialect in its natural, written, and spoken contexts.
Repetition – keep practicing after listening to the Egyptian dialect
Repetition is fundamental in mastering a language or dialect, emphasizing the importance of continually revisiting learned material. At Playaling, this principle is brought to life through a variety of exercises and tests accompanying their educational content. By regularly engaging with these materials, learners can deeply embed the nuances of Egyptian Arabic into their memory. Playaling’s structured approach ensures that repetition is not merely rote but a pathway to genuine familiarity and retention, making the learning process both effective and rewarding.
Watch real world Egyptian videos
Learning with real world Arabic videos not only enhances linguistic skills but also deepens cultural understanding. Playaling carefully selects videos covering all essential topics and aspects of Egyptian culture, lifestyle, common and uncommon ideas, customs, and traditions. Accompanied by transcripts and exercises, this immersive approach makes learning engaging and effective, connecting language learners directly with the heart of Egyptian culture and communication.
Connecting Egyptian Arabic learning with entertainment
Integrating entertainment into language learning combats boredom and enhances retention, especially with languages. To avoid boredom and prevent a slow down in learning over time, it’s essential to add some fun and entertainment when learning a new language. Recognizing this, Playaling infuses fun into learning Egyptian Arabic through a variety of engaging exercises. This approach ensures that learners not only acquire the language but also enjoy the process, leading to more effective learning outcomes. By offering content that delights as well as educates, learners are more likely to remember what they’ve learned, making the journey to fluency in Egyptian Arabic both joyful and rewarding.

Why learn Egyptian Arabic with Playaling?
Playaling stands out as the premier platform for mastering Egyptian Arabic, thanks to its unique blend of real-world video content and interactive exercises designed for learners at all proficiency levels. Unlike other resources that may offer limited dialectal focus, Playaling specifically targets the nuances of the Egyptian dialect.
Our platform harnesses the power of multimedia, including conversational videos, series, music, and more, to immerse learners in the language and guide you through the learning process. With Playaling, the journey to fluency is not only educational but also engaging, integrating entertainment into the curriculum to ensure a memorable and enjoyable learning experience.
This is achieved through:
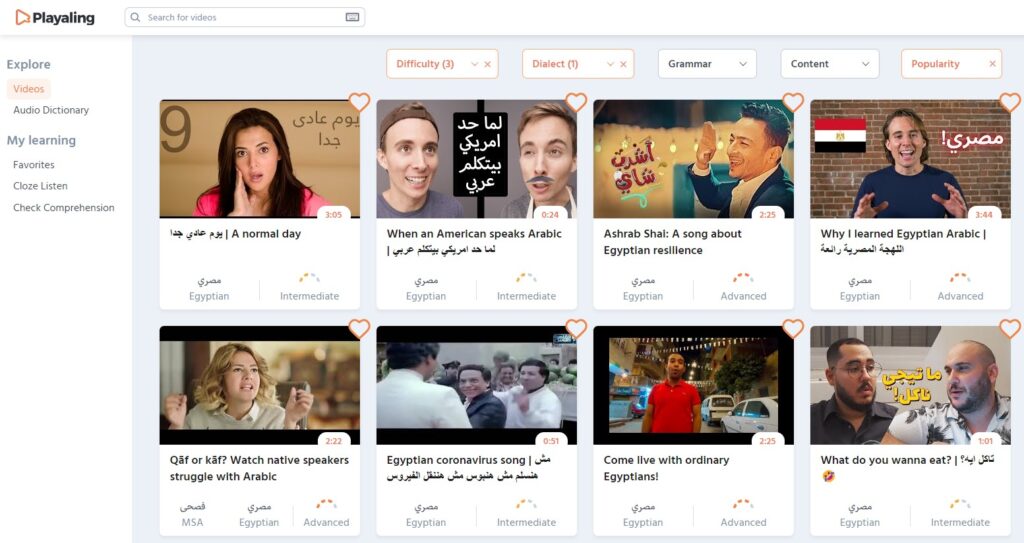
Real life Egyptian Arabic videos
Accompanied by transcripts for every word spoken in the video, these videos are enhancing understanding by linking spoken words to their written counterparts. This approach caters to learners of all levels and interests. Check these videos:
An interactive pronunciation popup
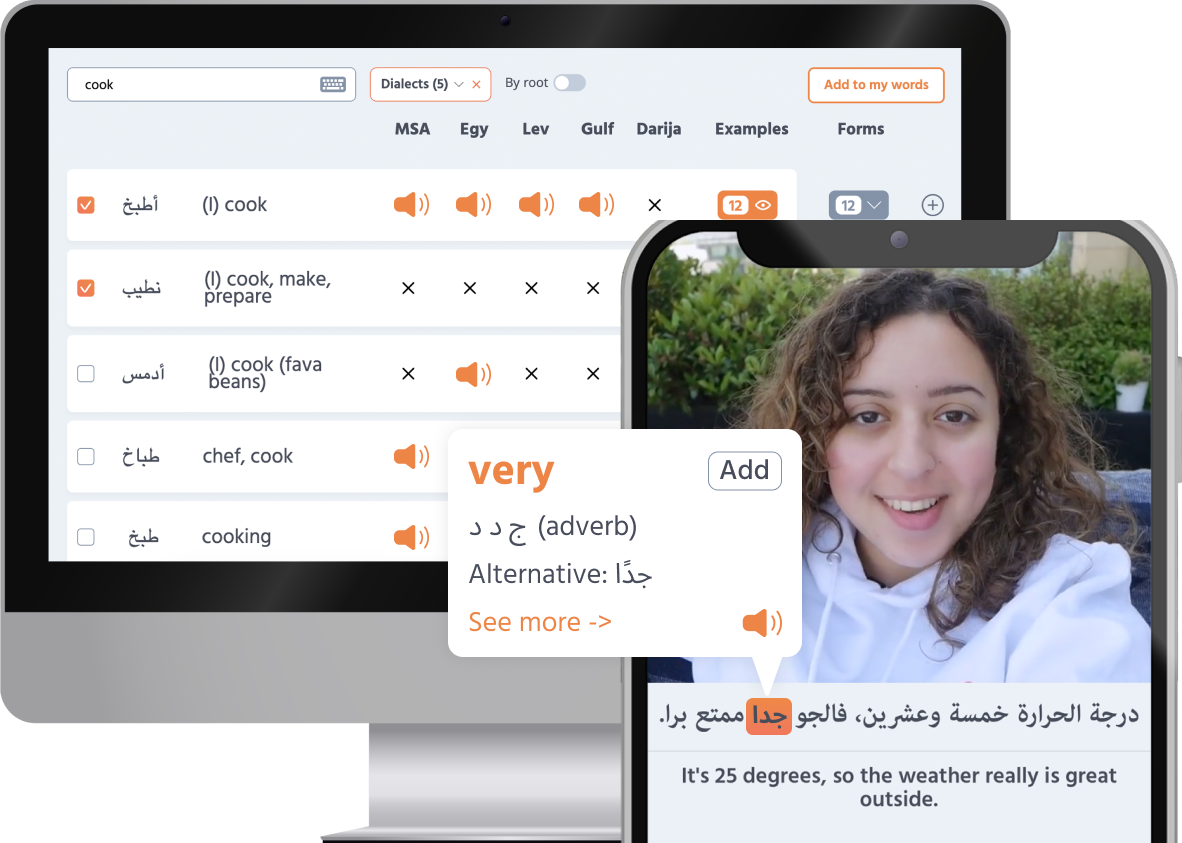
This feature enables you to click on any word to hear its pronunciation articulated by a native Egyptian speaker (not synthesized speech), offering examples of usage, along with definitions and meanings.
Engaging exercises
Activities and games designed to enhance understanding when listening to videos (fill in the blanks, multiple-choice questions).
An Audio Dictionary with Egyptian Arabic
This one-of-a-kind dictionary showcases word pronunciations, usage examples, and detailed definitions and meanings.
The strategic approach our platform employs makes learning new languages not only faster but also more delightful, especially for dialect acquisition.
For those keen on acquiring or advancing in the Egyptian dialect, you can visit the following sections to start learning this widely spoken dialect or to enhance your skills and expand your vocabulary:
- Real world videos in Egyptian dialect
- Audio Dictionary to look up any Egyptian word, hear it, and see it used in context
- Downloadable PDFs to download captions for any video in Egyptian Arabic
- Gap-fill exercise to train your ear by typing what you hear or selecting from a word bank
- Integrated listening comprehension that tests your understanding while you watch
The main differences between Egyptian dialect and Standard Arabic
The Egyptian dialect is influenced by Classical Arabic, French, Italian, Greek, Turkish, English, Coptic, which was the official language in Egypt before the Arab conquest in the 7th century AD. While debates persist regarding the classification of the Egyptian dialect—some advocating for its recognition as a distinct language—it remains officially categorized as a dialect of Arabic.
Egyptians will typically understand you if you communicate with them in Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) but may laugh or look at you curiously since it would be like someone trying to speak with you in Shakespearean English. Moreover, an Egyptian would be likely to respond to you in Egyptian Arabic, so if you didn’t know Egyptian, you wouldn’t understand their response. As a result, learning Egyptian Arabic is essential if your goal is to connect with Egyptian people.
The main differences between Egyptian Arabic and Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) include:
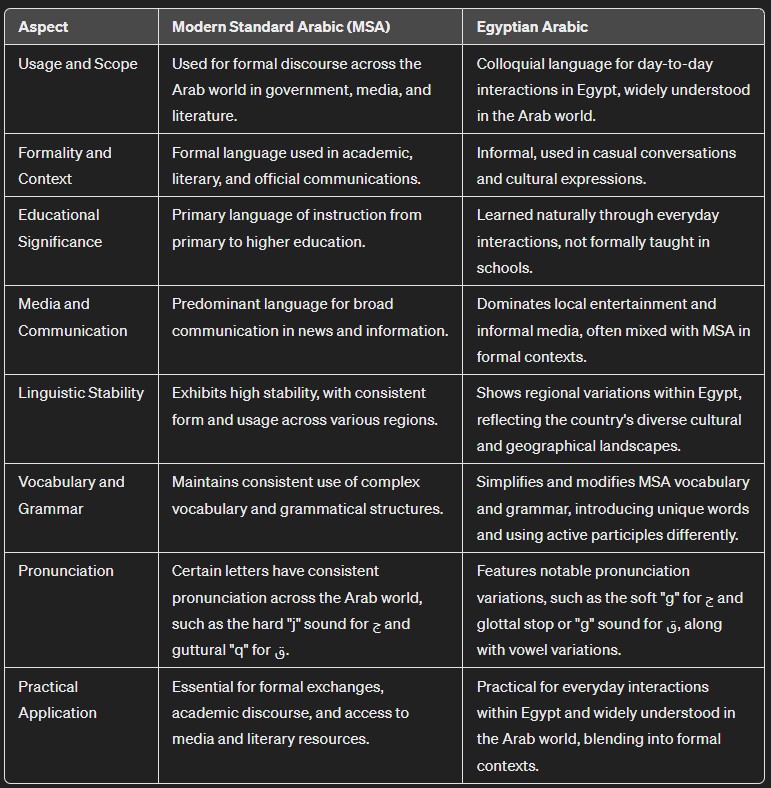
Usage and scope
- Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) assumes an important role across the Arab nations, being the preferred medium for formal discourse. This includes governmental documents, literary compositions, and various media forms.
- Egyptian Arabic holds a colloquial foothold within Egypt, serving as the lingua franca for day-to-day interactions. Its prominence extends beyond the national borders, garnering widespread comprehension and appreciation across the Arab world. This can be attributed to its significant representation in the spheres of media and entertainment, where Egyptian films, television shows, and music transcend local boundaries, embedding the dialect into the collective Arab consciousness. Through this cultural exchange, Egyptian Arabic not only enriches the region’s linguistic diversity but also fosters a shared understanding among Arab communities. Egyptian Arabic is so dominant that many educated Egyptians always only speak Egyptian Arabic, even in formal contexts.
Formality and context
- Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) is recognized for its structured elegance, predominantly employed within academic circles, literary discourse, and official communications. Its formal register makes it the linchpin of scholarly pursuits, governmental operations, and the literary world, serving as a bridge that links varied Arabic-speaking communities through a standardized linguistic platform. That being said, many Egyptians continue speaking Egyptian Arabic even when the context may call for more formal language.
- Egyptian Arabic thrives in the realm of informality, acting as the spontaneous voice of daily life and cultural articulations. Embedded in every greeting, marketplace haggle, and familial exchange, it pulsates through the social fabric of Egypt, offering a vibrant tapestry of expressions reflective of the nation’s heart and soul. Beyond the borders of Egypt, its influence permeates through cultural exports, including cinema, music, and television, making it a familiar companion in the daily lives of people across the Arab world. Through Egyptian Arabic, the nuances of Egypt’s rich cultural heritage are communicated, celebrating the idiosyncratic beauty found in everyday interactions and cultural expressions.
Educational significance
- Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) is upheld as the primary language of instruction. This protocol extends across the breadth of the educational landscape, from primary schools to the halls of higher education, such as universities. The adoption of MSA as a uniform medium for pedagogy ensures that a standardized version of Arabic is disseminated, facilitating a coherent educational framework that transcends regional dialectical differences.
- Egyptian Arabic, though not included in formal educational curriculums, is the native language of most of Egypt’s 110 million plus inhabitants,who acquire through everyday interactions and immersion in the cultural life of Egypt. This learning process can occurs naturally if individuals engage with the language in its authentic contexts—such as through conversation, media, or real world videos—allowing for a deep, intuitive understanding of the dialect.
Media and communication
- Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) serves as the predominant language. Its formal tone and widespread understanding across the Arab world make it a good choice for communicating news and information to a broad audience.
- Egyptian Arabic finds its stronghold within the more localized domains of entertainment, including television programming, cinema, musical productions, and theatrical performances. It is also common for Egyptian guests on news networks to speak in pure Egyptian dialect or a more formal version of Egyptian dialect mixed with MSA. This dialect’s widespread use in popular media not only reflects its deep-rooted cultural significance but also enhances its accessibility and appeal to the general public within Egypt and beyond.
Linguistic stability
- Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) exhibits a high degree of stability, maintaining consistency in form and usage across various Arab regions. Its structured nature allows for a uniform linguistic experience, facilitating communication and understanding on a broad scale.
- Egyptian Arabic displays a rich tapestry of regional variations within the country. These nuances reflect the diverse cultural and geographical landscapes of Egypt, resulting in slight variations in dialect that enrich the language with depth and variety.
Vocabulary and grammar
- Before you learn Egyptian Arabic, you should know it frequently modifies and streamlines the vocabulary and grammatical structures common to Modern Standard Arabic (MSA). For example, the demonstratives هَذَا / ذا (this, masculine) and هَذِهِ / ذي (this, feminine) in MSA are respectively transformed into دَه and دِي in Egyptian dialect.
- Egyptian Arabic introduces unique lexical items for commonly used words. For instance, the interrogative مَاذا (what) in MSA is replaced with إيه in Egyptian Arabic, showcasing a distinctive approach to forming questions.
Another significant difference lies in the use of active participles (or pseudo verbs in the form of اسم فاعل ) within the Egyptian dialect, a feature that markedly distinguishes it from MSA.
For example: In Modern Standard Arabic (MSA), you might say: أنا أحب (meaning “I like”) where أحب is a present tense verb. In Egyptian Arabic, however, you may say أنا بحب (the direct equivalent) or instead you may say أنا حابب , which means the same thing.
This example illustrates Egyptian Arabic’s dynamism and flexibility in communication. Instead of relying solely on traditional verb forms, speakers can employ active participles directly as verbs to express actions more dynamically.
Pronunciation
Pronunciation variations are a key differentiator between Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) and Egyptian Arabic, especially in the articulation of specific consonants and vowels. These phonetic discrepancies play a crucial role in shaping the unique sound profile of the Egyptian dialect.
One notable deviation is the pronunciation of the letter ج in MSA, which is typically pronounced as a hard “j” sound, akin to the English ‘j’ in “job” In contrast, Egyptian Arabic often renders this consonant as a softer “g” sound, similar to the ‘g’ in “go.” This alteration affects a myriad of common words, thereby distinguishing Egyptian speech patterns from those of MSA. However, in Upper Egypt (southern Egypt), the classical “j” sound remains intact.
Another example involves the treatment of the letter ق . In MSA, ق is articulated from the back of the throat with a deep, guttural sound . However, in typical Egyptian Arabic, this sound is softened or transformed into a glottal stop (similar to the catch in the throat in the middle of “uh-oh”). In Upper Egypt (southern Egypt), the qāf may transition into a hard “g” sound like in the word “go”.
Vowel pronunciation and length also exhibit differences.
MSA features a clear distinction between short and long vowels which can change the meaning of words. While Egyptian Arabic also distinguishes between short and long vowels, the application and influence on meaning can be more fluid, and in some cases, long vowels in MSA might be shortened or slightly modified in Egyptian Arabic, adding to the dialect’s unique sound.
These phonetic nuances not only underscore the linguistic diversity within the Arab world but also highlight the richness and adaptability of the Arabic language shaped by regional and cultural influences.
Practical Application
Acquiring proficiency in Egyptian Arabic holds considerable practical benefits for day-to-day interactions not only within Egypt, but also throughout the Arab world, since the vast majority of Arabs understand it. It’s also indispensable for understanding the majority of Egyptians, since most maintain a heavy dose of Egyptian dialect at all times, even when speaking spontaneously in formal contexts.
Conversely, Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) stands as a fundamental tool for formal exchanges, its significance extending to the comprehension of news and information disseminated through media channels across the Arab world. MSA’s structured formality and pan-Arab recognition make it a universal medium for official communications, academic discourse, and access to a vast array of literary and scholarly resources.
To summarize, Modern Standard Arabic embodies the formal linguistic framework that underpins official, educational, and media-related communication throughout the Arab region. In contrast, the Egyptian Arabic dialect holds greater sway in daily life, commanding a strong presence in Egypt’s everyday conversations and enjoying widespread utilization in Arab entertainment and media. This distinction highlights the complementary roles of both language forms, catering to a spectrum of communication needs from formal to informal settings, and facilitating a more comprehensive engagement with Arab cultures and societies.

Why learn the Egyptian dialect?
With a population of over 115 million, Egypt is by far the largest Arab country, and Cairo, its capital, with a population of over 20 million, is the largest Arab city. Consequently, Egyptian Arabic speakers are more numerous than the speakers of any other dialect. Moreover, Egypt, with its rich history, is a tourist destination that attracts people from around the world. Those who learn to speak Egyptian will undoubtedly gain much enjoyment and benefit when visiting and exploring the country.
The impact of the Egyptian dialect extends beyond Egypt to the Arab world. Most Arabs understand this dialect due to its widespread use in songs, television programs, cinema, theater, and even in some novels and various forms of poetry. Egypt has been a pioneer in participating in radio, television, and theater since its inception, leaving a significant influence of its dialect on all Arabs. So if you don’t learn Egyptian colloquial Arabic, you miss a lot.
Here are some examples of famous works in Egyptian dialect:
Fascinating information about ancient Egypt
When learning a language, it is essential to acquire some information about the country or region where the language is spoken, including its history and civilization. If you are interested in learning Egyptian Arabic, you are most likely interested in the well-known history of Egypt.
Ancient Egyptians established the world’s first peace treaty
They engaged in prolonged wars lasting two centuries with the Hittite Empire, resulting in no clear victory. When Pharaoh Ramesses II came to power in 1279 BC, he signed a peace treaty with Hittite Emperor Hattusili III. According to this treaty, the conflict between the two sides ended, and they pledged to stand united against any common enemy threatening the territories of either empire.
Spread of board games in ancient Egypt
Ancient Egyptians used to play board games and table games after work. They organized competitions in these games, with one of the most famous being known as “Senet,” dating back to 3500 BC.
Independence and rights of Egyptian women
Women in ancient Egypt enjoyed full rights in buying, selling, trading, filing lawsuits, divorce, and remarriage. This was distinctive and uncommon at the time, as Greek civilization considered women the property of their husbands.
Workers’ strike
Despite the pharaoh being considered a deity, this did not deter workers from demanding their rights and expressing grievances. Egyptian workers organized a strike protesting the non-receipt of their regular wages during the construction of the royal tomb in the era of Ramesses III. This strike is considered one of the earliest recorded in human history.
Slaves did not build Egypt’s pyramids
The pyramids of Egypt were built by skilled and paid craftsmen, not slaves.
The presence of specialized physicians
During that period, general medicine was prevalent, but in ancient Egypt, there were specialized physicians for specific diseases, such as dentistry, ophthalmology, and digestive issues.
Adornment by women and men
Beauty held great importance in ancient Egyptian civilization and was a part of their religious practices. Therefore, both men and women used makeup and dyes to adorn their nails and hair.
Pet ownership
Ancient Egyptians loved animals and considered them embodiments of certain deities. They kept them in their homes, mummified them, and buried them with their owners, including cats, dogs, lions, and falcons.
You can subscribe for Playaling and experience all available features without any restrictions for a free trial period of 7 days. Afterward, you can decide whether to continue and pay for your subscription or cancel, with no charges incurred. We can guarantee you a distinctive learning experience, free from boredom. You will see this when you subscribe to the platform and explore the diverse content. We wish you a unique educational journey in the fascinating world of Arabic and its dialects.
Table of Contents
Links
Links